Statistics, Cybersecurity [Year 2021 - 22]
Topics on Statistics with intensive computer applications
$ \int_0^t d S_u = \int_0^t \mu(S_u, u) du + \int_0^t\sigma(S_u, u) dW_u $
Supporto al corso e alla didattica telematica, by T. Gastaldi #Sapienzanonsiferma #Sapienzadoesnotstop
(Instructor: tommaso.gastaldi@gmail.com,
https://www.datatime.eu/public/cybersecurity/)
Whatsapp group for the students of this course
Invitation to join the Whatsapp group for this course:
https://chat.whatsapp.com/Kk3wRGmmxWH9RNUo01zFdX
(work group for communication exchange about the course and exams. When first joining, send a message with your name and id ("matricola"))
Students research blogs: [write your link in the google sheet]
each student will create his/her own free blog, eg. with any free blogging platform, to publish their hypertext essays [for the oral exam], and
indicate the link in the google sheet we have prepared)
VOLUNTARY WORK GROUPS created by students
[to be filled]
________________________________________________________________________________________
- LESSON 01 - [23 Sept 2021]
VIDEO LESSONS:
Course Introduction
Lesson_01_Intro_01_Welcome_CourseStructure_Exams https://drive.google.com/file/d/1OFWq9cpEyIfk7qcPBVF_kX1IILYVkn8m/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_01_Intro_02_OralExam_YourBlog https://drive.google.com/file/d/1_7tICctUq7lHXWTFjlHfgG_6kWvkuBxq/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_01_Intro_03_WrittenExam_YourIDE https://drive.google.com/file/d/1g6KQbvuNNwCEFdr0L0gebCNas1DfByAP/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_01_Intro_04_LessonWorkFlow_HowtoCiteYourSources https://drive.google.com/file/d/10ZiwDmOJelY4AmCKU0L8u9oII38VqcMl/view?usp=sharing
Theory
Lesson_01_Theory_01_DataSetDefinition_Population_Attributes https://drive.google.com/file/d/1B1MUKNXEbrYmMuZTNPf-SObLwCxhD3Hp/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_01_Theory_02_DescriptiveAndInferentialStatistics https://drive.google.com/file/d/1C7JIf1d5a5W_Pa3M18Zp6WQqySESQFsN/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_01_Theory_03_UnivariateAndMultivariateStatistics https://drive.google.com/file/d/17kjGwE-S5NDuLhmQUcexvDXAyntireof/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_01_Theory_04_FirstUnivariateExample_TowardTheDistribution https://drive.google.com/file/d/1mEmOTQkJ4sX4pYB3OoxdrEVts0JD8YBS/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_01_Theory_05_ImportanceOfDistribution https://drive.google.com/file/d/18qR73tUfm9-Nm869UAAW12UvytKS4T0C/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_01_Theory_06_EmpiricalUnivariateDistribution https://drive.google.com/file/d/1WkQVYbkofjAQlChoWbPstEUT9p_QcUrL/view?usp=sharing
Computer applications, and language fundamentals for statistical algos
Lesson_01_Apps_01_IntroductionToVSAndLanguages https://drive.google.com/file/d/1LFZQGsBxqWb8q80sgrlqLLWRVjusneRV/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_01_Apps_02_CreateAVisualStudioProject https://drive.google.com/file/d/1LSw8cNdbni-AOLk71dcfWa7PTbprlhci/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_01_Apps_03_RunYourVeryFirstPrograms https://drive.google.com/file/d/1BVDwkJUPOkti79MCNg4EVsPFJYelaLHW/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_01_Apps_04_WinformsAndObjectProperties https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Zs4QDdTdFGfxXuFF0v1t-YimdynEfaoc/view?usp=sharing
Extra material (optional)
Lesson_01_Apps_05_OOP_EventDriven https://drive.google.com/file/d/1goukDbMRgaDMfd6nvcpyEGMI-cyZRcmy/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_01_Apps_06_CreatingObjects_Definition_Instantiation https://drive.google.com/file/d/1gQZY5jUloOK8_zuV21iqgWgCcMfujTLr/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_01_Apps_07_CreatingObjects_PracticalExamples https://drive.google.com/file/d/1DIgrwpiENQnqPZJ5_N_ldGhlvFhkLyox/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_01_Apps_08_ReferenceAndValueTypes https://drive.google.com/file/d/1HZ4vu0dVx8VJDM0X4Hmg7YoduBIJTjwp/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_01_Apps_09_ReferenceAndValueTypes_SimpleDemo https://drive.google.com/file/d/1DxhvyOYYsj8ETq36kqCZ66Eaxq5ayQm-/view?usp=sharing
HOMEWORK / ASSIGNMENTS (to be published by the student on the personal
blog) : [DATE DUE: post your link within 3 Oct 2021 or -1 penalty on
final grade may apply]
Researches about theory (R)
1_R. Give your best description of the many reaching out of statistics, in its various form, as a branch of math (Probability theory, etc.), as a set of methodologies used in many other disciplines, as an essential tool to deal with any sort of data, make reports and provide governance tools. Discuss whether it can be considered a "science" and what is the "scientific method" (what is a "theory" and what is a "hypothesis"). What is the role of Statistics in Math and Science ?
Applications / Practice (A)
1_A. Create - in both languages C# and VB.NET
(and optionally in js) -
a program which does the following simple tasks to get acquainted with the tool:
-
when a button is pressed some text appears in a richtexbox on the startup form
-
when another button is pressed animate one or more balls (possibly of different
colors and sizes) within a
rectangle
OPTIONAL (web version)
Do the same using plain js/html/css (simple examples in:
https://www.datatime.eu/public/cybersecurity/JSTutorial/ )
REFERENCES / SOURCES / USEFUL LINKS
Platform to publish your weekly homework:
Choose your free blogging platform: https://www.wpbeginner.com/beginners-guide/how-to-choose-the-best-blogging-platform/ ,
https://www.creativebloq.com/web-design/best-blogging-platforms-121413634
Always cite your sources and give proper credits (this is useful for both
avoiding plagiarism, but also declining responsibility for possible errors in
the sources): https://www.plagiarism.org/article/how-do-i-cite-sources
Additional useful readings on statistical theory:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Statistical_unit
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unit_of_observation
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Statistical_population
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Variable_and_attribute_(research ), https://stattrek.com/descriptive-statistics/variables.aspx , https://study.com/academy/lesson/defining-the-nature-of-an-attribute-being-measured.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_set
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sample_(statistics)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Descriptive_statistics
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Statistical_inference , https://statistics.laerd.com/statistical-guides/descriptive-inferential-statistics.php
Frequency distribution:
https://www.stat.uci.edu/what-is-statistics/#:~:text=Statistics%20is%20the%20science%20concerned,interpreting%20and%20presenting%20empirical%20data.&text=Any%20measurement%20or%20data%20collection,number%20of%20sources%20of%20variation.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/terms/statistics.htm
https://www.quora.com/Is-statistics-a-science
https://www.quora.com/Is-statistics-math-or-science
https://www.quora.com/What-is-the-difference-between-mathematics-and-statistics
https://www.reddit.com/r/askscience/comments/3ra1su/why_is_string_theory_a_theory_in_science_doesnt/
...
For applications:
Download your IDE (include C# and VB.NET): https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/it/downloads//
Example of VB.NET c# comparison table: https://sites.harding.edu/fmccown/vbnet_csharp_comparison.html
Example of code converter: https://codeconverter.icsharpcode.net/
Case styles: https://medium.com/better-programming/string-case-styles-camel-pascal-snake-and-kebab-case-981407998841
Format Shortcut: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/4942113/is-there-a-format-code-shortcut-for-visual-studio#:~:text=To%20answer%20the%20specific%20question,F%20to%20format%20the%20selection
Programming paradigms, OOP: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Programming_paradigm
Event driven programming: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Event-driven_programming
Object class: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/system.object?view=netcore-3.1
Inheritance: https://medium.com/@andrewkoenigbautista/inheritance-in-object-oriented-programming-d8808bca5021
Value types vs Reference types: https://docs.microsoft.com/it-it/dotnet/csharp/language-reference/builtin-types/value-types , http://net-informations.com/faq/general/valuetype-referencetype.htm , https://www.c-sharpcorner.com/article/C-Sharp-heaping-vs-stacking-in-net-part-i/ , https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/1204612/How-string-Behaves-Like-Value-Type-as-it-is-refere
Value type: https://docs.microsoft.com/it-it/dotnet/api/system.valuetype?view=netcore-3.1
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/23345554/the-differences-between-initialize-define-declare-a-variable
For Blogs:
https://www.websiteplanet.com/blog/business-blogging-statistics/
Programming courses (link sent by company):
https://www.futurelearn.com/subjects/it-and-computer-science-courses/coding-programming
______________________________________________________________________________________
-
LESSON 02 - [30 Sept 2021]
VIDEO LESSONS:
Theory
Lesson_02_Theory_01_AttributeOperationalization_ScaleOfMeasurement https://drive.google.com/file/d/1MotGvQALCv0RSI9m_qU3SBckHZb3m7cF/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_02_Theory_02_CategoricalAndQuantitativeVariables https://drive.google.com/file/d/1ehacAHXb5eaBN99l_1siNHj_3huHUfBY/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_02_Theory_03_TimeSeriesAnalysis https://drive.google.com/file/d/1-IJ280tHTn78Le8vpiAItvO9eO80cjs1/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_02_Theory_04_SpacialDataAnalysis https://drive.google.com/file/d/1UFGQ3arfpeHFYgiIx0FvqXF0cqrVwLIX/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_02_Theory_05_StatisticalDataInRealWorld_DW_OLTP_Olap https://drive.google.com/file/d/1WMI-N4Swi6lnXWD7KHYOLE_Yvp8RGtwX/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_02_Theory_06_StreamAndBatchProcessing_Intro_DataStreaming https://drive.google.com/file/d/1pVZZ23inf5wFiFsop1y-ZY4zoj9ebeKD/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_02_Theory_07_StreamAndBatchProcessing_Intro_OnlineOffline https://drive.google.com/file/d/115LNBHnjQfUYPDFJOOToGVEHxEKUNS0e/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_02_Theory_08_StreamAndBatchProcessing_Intro_Collections_Random_Timer https://drive.google.com/file/d/1-nxFZ488KyyRoSLqstxnTS06FWuw9kjy/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_02_Theory_09_StreamAndBatchProcessing_Intro_AverageAsRepresentativeValue https://drive.google.com/file/d/1oOnXX9W7gWkUchTpYXKPvxmMQ3L-mpEl/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_02_Theory_10_StreamAndBatchProcessing_Intro_Metadata https://drive.google.com/file/d/1nysLtwfxahZyagsLeA_S85_4BOYpWdEo/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_02_Theory_11_StreamAndBatchProcessing_Intro_RawDataToObjects https://drive.google.com/file/d/1wLmmIesCiFdOkkMLZmChEibryfnLKmni/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_02_Theory_12_StreamAndBatchProcessing_KnuthOnlineAlgo https://drive.google.com/file/d/1LmzG2uKSO4X782XQ8w0n57emJxXxHirl/view?usp=sharing
Computer applications, and language fundamentals for statistical algos
Lesson_02_Apps_01_StreamAndBatchProcessing_BatchExample_Random_List https://drive.google.com/file/d/1AazPlPpEwo35DQkT7_xgLKuriGRgiSue/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_02_Apps_02_StreamAndBatchProcessing_StreamExample_OnlineAlgo https://drive.google.com/file/d/14i5P3-FBagNwyRLx36Xhdofo2AWmiJ-h/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_02_Apps_03_ImportanceOfMeanOnlineAlgo_IssuesWithFloatingPoint https://drive.google.com/file/d/1iApjQUliWs8Qm66yfVqzLSwFRE9-w7rq/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_02_Apps_04_UnivariateDistribution_DiscreteVariable https://drive.google.com/file/d/14RNJguDeBaw0EXi4H2H64eyzmFRddDt3/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_02_Apps_05_UnivariateDistribution_ContinuousVariable https://drive.google.com/file/d/1XelrkJC8qfDycuNmWkZNd5vEsMco7xjJ/view?usp=sharing
Extra help to clean up code (optional material):
OPT
Lesson_02_Apps_06_RefactoringExample_NeedForModularity https://drive.google.com/file/d/1wOT7fn60ndCOvVsOR9T4IUTD47fRYTsh/view?usp=sharing
OPT Lesson_02_Apps_07_RefactoringExample_Maintanability https://drive.google.com/file/d/1ne8uwE5oYW7GwuqZWoTYXgnFKM0pN5mR/view?usp=sharing
OPT Lesson_02_Apps_08_RefactoringExample_Linq_LambdaExpressions https://drive.google.com/file/d/1mtv9UT6azakrQFZlbqSyUHFyyCHW6TMU/view?usp=sharing
OPT
Lesson_02_Apps_09_RefactoringExample_Reusability https://drive.google.com/file/d/1ISl9eK3QPBb1vrn7pj2yHLLtAEUmYgxk/view?usp=sharing
HOMEWORK / ASSIGNMENTS (to be published by the student on the personal
blog) : [DATE DUE: post your link within 10 Oct 2021 or -1 penalty on
final grade may apply]
Researches about theory (R)
2_R. Describe the most common configuration of data repositories in the real
world and corporate environment. Concepts such as Operational or Transactional
systems (OLTP), Data Warehouse DW, Data Marts, Analytical and statistical
systems (OLAP), etc. Try to draw a conceptual picture of how all these
components may work together and how the flow of data and information is
processed to extract useful knowledge from raw data.
3_R. Show how we can obtain an online algo for the arithmetic mean and explain the various possible reasons why it is preferable to the "naive" algo based on the definition.
Applications / Practice (A)
2_A. Create - in both languages C# and VB.NET -
a demonstrative program which computes the online arithmetic mean (if it's a
numeric variable) and your own algo to compute the distribution for a discrete
variable and for a continuous variable (can use values simulated with RANDOM
object).
3_A. Create an object providing a rectangular area which can be moved and
resized using the mouse. This area will hold our future charts and graphics.
OPTIONAL
Do the last exercise
3_A as web app, in javascript/html/css.
(simple
examples in:
https://www.datatime.eu/public/cybersecurity/JSTutorial/ ))
Researches about applications (RA)
1_RA. Understand how the floating point representation works and describe systematically (possibly using categories) all the possible problems that can happen. Try to classify the various issues and limitations (representation, comparison, rounding, propagation, approximation, loss of significance, cancellation, etc.) and provide simple examples for each of the categories you have identified (e.g.,, https://floating-point-gui.de/basic/ , https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E19957-01/806-3568/ncg_goldberg.html , http://indico.ictp.it/event/8344/session/50/contribution/207/material/slides/0.pdf , https://stackoverflow.com/questions/2100490/floating-point-inaccuracy-examples , etc.)
REFERENCES / SOURCES / USEFUL LINKS:
Additional useful readings on statistical theory:
Operationalization: https://explorable.com/operationalization#:~:text=Operationalization%20is%20the%20process%20of,be%20measured%2C%20empirically%20and%20quantitatively ., https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Operationalization
Level of measurement: https://www.questionpro.com/blog/nominal-ordinal-interval-ratio/ , https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Level_of_measurement , https://byjus.com/maths/categorical-data/ , https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Categorical_variable
Order relation: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Order_theory
Unit of observation / Data Point: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unit_of_observation#Data_point
Class interval: https://internal.ncl.ac.uk/ask/numeracy-maths-statistics/statistics/descriptive-statistics/class-intervals-and-boundaries.html#:~:text=Definition,only%20one%20observation%20per%20interval
Table: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Table_(database)#:~:text=In%20relational%20databases%2C%20and%20flat,have%20any%20number%20of%20rows .
Database: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Database
More on database and relational data: https://www.khanacademy.org/computing/computer-programming/sql/relational-queries-in-sql/a/splitting-data-into-related-tables
Time Series Analysis: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Time_series#:~:text=Time%20series%20analysis%20comprises%20methods,based%20on%20previously%20observed%20values
Arrow of time: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arrow_of_time
Spatial Data Analysis: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spatial_analysis
Matrices: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Matrix_(mathematics )
Vectors: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Row_and_column_vectors
Streaming Data: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Streaming_data
Data Lake (Data Swamp): https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_lake
OLTP: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Online_transaction_processing
Data Warehouse (DW): https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_warehouse
Data Mart: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_mart
On Line Analytical Processing (OLAP): https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Online_analytical_processing
Data Analysis: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_analysis
Data Mining: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_mining
Data Reporting: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_reporting
Predictive Analytics: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Predictive_analytics
Streaming algorithms: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Streaming_algorithm
Online algorithm: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Online_algorithm
Online Vs Offline: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/11496013/what-is-the-difference-between-an-on-line-and-off-line-algorithm
One-pass algorithm: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/One-pass_algorithm#:~:text=In%20computing%2C%20a%20one%2Dpass,the%20size%20of%20the%20input ., https://stackoverflow.com/questions/26322007/what-is-a-single-pass-algorithm
One-pass Vs Online: https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/396728/what-is-the-diffrences-between-online-and-one-pass-learning
One-pass Vs Multi-pass: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/58407978/difference-between-one-pass-and-multi-pass-computations
Stream Processing: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stream_processing, https://hazelcast.com/glossary/stream-processing/
Event Stream Processing: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Event_stream_processing , https://hazelcast.com/glossary/event-stream-processing/
Data Buffer: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_buffer
Batch / Micro Batch Processing: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Batch_processing, https://hazelcast.com/glossary/micro-batch-processing/
Metadata: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metadata
Pseudocode: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pseudocode
For applications
Collections and Data Structures: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/standard/collections/
https://stackoverflow.com/Questions/128636/net-data-structures-arraylist-list-hashtable-dictionary-sortedlist-sorted
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1427147/sortedlist-sorteddictionary-and-dictionary
List: https://www.dotnetperls.com/list-vbnet , http://vb.net-informations.com/collections/list.htm
Dictionary: https://www.tutorialsteacher.com/csharp/csharp-dictionary , http://vb.net-informations.com/collections/dictionary.htm
Sorted Dictionary: https://docs.microsoft.com/it-it/dotnet/api/system.collections.generic.sorteddictionary-2?view=netcore-3.1 , https://www.dotnetperls.com/sorteddictionary
Sorted List: https://docs.microsoft.com/it-it/dotnet/api/system.collections.sortedlist?view=netcore-3.1 , https://www.tutorialsteacher.com/csharp/csharp-sortedlist , https://www.dotnetperls.com/sortedlist-vbnet
KeyValuePair: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/system.collections.generic.keyvaluepair-2?redirectedfrom=MSDN&view=netcore-3.1
Floating point: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Floating-point_arithmetic , https://stackoverflow.com/questions/18409496/is-it-52-or-53-bits-of-floating-point-precision
Floating point issues: https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E19957-01/806-3568/ncg_goldberg.html ,
https://www.volkerschatz.com/science/float.html , https://floating-point-gui.de/ , https://csharpindepth.com/Articles/FloatingPoint .
Decimal floating point: https://csharpindepth.com/Articles/Decimal , https://stackoverflow.com/questions/618535/difference-between-decimal-float-and-double-in-net
Loss of significance, catastrophics cancellation: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Loss_of_significance
Fixing sums: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kahan_summation_algorithm
Integer division: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/661028/how-can-i-divide-two-integers-to-get-a-double
For/For each loop: https://www.tutorialsteacher.com/csharp/csharp-for-loop
Do Loop: https://www.tutorialsteacher.com/csharp/csharp-do-while-loop
If Then Else: https://www.tutorialspoint.com/vb.net/vb.net_if_else_statements.htm , https://www.dotnetperls.com/if-vbnet
My quick summary of control structures (ita): StruttureControlloFlusso.txt (send changes if you see inaccuracies, things to add/improve)
Reusability, Maintanability, Modularity, Performance: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reusability, http://singlepageappbook.com/maintainability1.html#:~:text=Modular%20code%20is%20code%20which,not%20just%20about%20code%20organization . https://press.rebus.community/programmingfundamentals/chapter/modular-programming/ , https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1444221/how-to-make-code-modular , https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Modular_programming , http://www.jrobbins.org/ics121f03/lesson-maintain.html , https://softwareengineering.stackexchange.com/questions/279140/performance-versus-reusability , ...
LINQ: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/csharp/programming-guide/concepts/linq/ , https://www.tutorialsteacher.com/linq/linq-query-syntax , https://www.tutorialsteacher.com/linq/linq-method-syntax
Lambda expressions: https://www.tutorialsteacher.com/linq/linq-lambda-expression
Murphy Law: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Murphy%27s_law
Spaghetti code: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spaghetti_code
_______________________________________________________________________________________
-
LESSON 03 - [07 Oct 2021]
VIDEO LESSONS:
Note: "OPT"
indicates optional video material extra that can be skipped. Same for
homework, "OPT"
denotes homework that can be skipped.
Theory
Lesson_03_Theory_01_BivariateDistribution_Marginal_Conditional https://drive.google.com/file/d/1wgn-MDiG9H1FKFibCcTKyaTwYhSiKl-o/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_03_Theory_02_BivariateDistribution_ContingencyTable https://drive.google.com/file/d/1fo1xsPRNzrhmNThHN_NHXjozC3vFEfLU/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_03_Theory_03_BivariateDistribution_Bayes https://drive.google.com/file/d/1s6sf8JJJh_UsBs86TxON3uEt4udSEv-u/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_03_Theory_04_BivariateDistribution_StatisticalIndependence https://drive.google.com/file/d/1AK98i1qehD3CrvbEkYAb-0tiLuCpCtzf/view?usp=sharing
Computer applications, and language fundamentals for statistical algos
OPT Lesson_03_Apps_01_ReadingExternalDataSources_Intro https://drive.google.com/file/d/1WfqUhl_dftfnibnK_seLPFa-J39p8GFi/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_03_Apps_02_StreamReader_Field_Parser_FileDialog https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Woj01dQ8s_Ia2bUm6YdqiAGQa0yeaDHE/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_03_Apps_03_ReadingCSV_Example https://drive.google.com/file/d/1pkU4hwpIoSmTAwh04yI335kKfdonpdAr/view?usp=sharing
OPT Lesson_03_Apps_04_GeneralizingProgramsWithReflection https://drive.google.com/file/d/1-fqU1fc8rVYSDFsQO_Oyh0QuwL0sflFt/view?usp=sharing
OPT Lesson_03_Apps_05_BivariateDistribution_DiscreteVariable_GettingReady https://drive.google.com/file/d/1_Nawbiqw59aXPQ6R1TOXOT0Jo7WuLxdj/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_03_Apps_06_BivariateDistributionDiscrete_Computing https://drive.google.com/file/d/1aZZ8ZTVrgqLGwlnmTK5Tz38JjDgcYT_j/view?usp=sharing
OPT
Lesson_03_Apps_07_BivariateDistributionDiscrete_MakingTheContingencyTable https://drive.google.com/file/d/1VK3_qX5T8FBHiLNkouzGhJPc6rr0KVc7/view?usp=sharing
OPT
Lesson_03_Apps_08_BivariateDistributionDiscrete_MoreDetails_Hashset_SortedSet https://drive.google.com/file/d/10x_znFTmastvqai9Bw17VT1hkYPR8uRa/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_03_Apps_09_BivariateDistribution_ClassInterval https://drive.google.com/file/d/1JBRpM0CvMMZZ1f78Z7dmNp80JOrGcyeg/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_03_Apps_10_QuickIntroductionToGraphics https://drive.google.com/file/d/1PRTrnKlvbeCYWJ9S-hRSiJfEC8LFsPAi/view?usp=sharing
HOMEWORK / ASSIGNMENTS (to be published by the student on the personal blog) : [DATE DUE: post your link within 17 Oct 2021 or -1 penalty on final grade may apply]
Researches about theory (R)
4_R. Explain what are marginal, joint and conditional distributions and how we can explain the Bayes theorem using relative frequencies. Explain the concept of statistical independence and why, in case of independence, the relative joint frequencies are equal to the products of the corresponding marginal frequencies.
Applications / Practice (A) [work on this at least
30' a day, all days]
4_A. Create a program - in both languages C# and VB.NET (and
optionally in js) - to read data from a CSV file, and store it into suitably designed objects, for further processing. Compute mean and standard
deviation and frequency distribution for at least one of the variable, and for
one pair of variables.
5_A.
Compute - in both languages C# and VB.NET (and optionally in js) - a frequency distribution of the meaningful words
from any text file and create a personal graphical representation of the corresponding
"word cloud" (in case, can use animation if you wish), keeping into account the frequencies of the words.
(A file of italian stop words, in case might be useful:
https://datatime.eu/public/cybersecurity/jsTutorial/StopWords_Ita.txt:
please suggest more)
Researches about applications (RA)
2_RA. Do a review about charts useful for statistics and data presentation (example of some: StatCharts.txt ). What is the chart type that impressed you most and why ?
3_RA. Do a comprehensive research about the GRAPHICS object and all its members
(to get ready to create any statistical chart.)
REFERENCES / SOURCES / USEFUL LINKS:
Additional useful readings on statistical theory:
Bivariate distribution: http://www.brainkart.com/article/Bivariate-Frequency-Distributions_35069/#:~:text=In%20other%20words%2C%20a%20bivariate,students%20in%20an%20intelligent%20test.&text=Each%20cell%20shows%20the%20frequency%20of%20the%20corresponding%20row%20and%20column%20values.
Contingency table: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Contingency_table
Conditional relative frequency: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PHORXJSIm2k
Bayes: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XQoLVl31ZfQ , https://betterexplained.com/articles/understanding-bayes-theorem-with-ratios/
Independence: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZxzVfRiitM0
For applications
CSV: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comma-separated_values, https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4180 , https://www.loc.gov/preservation/digital/formats/fdd/fdd000323.shtml , https://www.thoughtspot.com/6-rules-creating-valid-csv-files
StreamReader: https://www.dotnetperls.com/streamreader, https://www.tutorialspoint.com/vb.net/vb.net_text_files.htm
TextFieldParser: https://docs.microsoft.com/it-it/dotnet/api/microsoft.visualbasic.fileio.textfieldparser?view=netcore-3.1 , https://stackoverflow.com/questions/22297562/csv-text-file-parser-with-textfieldparser-malformedlineexception
StreamWriter: https://www.dotnetperls.com/streamwriter-vbnet
HashSet https://docs.microsoft.com/it-it/dotnet/api/system.collections.generic.hashset-1?view=netcore-3.1
SortedSet https://docs.microsoft.com/it-it/dotnet/api/system.collections.generic.sortedset-1?view=netcore-3.1
Tuple: https://docs.microsoft.com/it-it/dotnet/api/system.tuple-2?view=netcore-3.1
Interface, Multiple inheritance: https://www.ict.social/vbnet/oop/interfaces-in-vbnet-course
Icomparable https://docs.microsoft.com/it-it/dotnet/api/system.icomparable?view=netcore-3.1
Type class: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/system.type?view=netcore-3.13.1
GetType / typeof http://net-informations.com/q/faq/type.html
Isnumeric: https://docs.microsoft.com/it-it/office/vba/language/reference/user-interface-help/isnumeric-function
, https://stackoverflow.com/questions/894263/identify-if-a-string-is-a-number , https://docs.microsoft.com/it-it/dotnet/csharp/programming-guide/strings/how-to-determine-whether-a-string-represents-a-numeric-value
Number/String checks: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/5311699/get-datatype-from-values-passed-as-string/5325687 , https://stackoverflow.com/questions/2751593/how-to-determine-if-a-decimal-double-is-an-integer , https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/13338/Check-If-A-String-Value-Is-
Parse datetime:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/919244/converting-a-string-to-datetimee, https://docs.microsoft.com/it-it/dotnet/api/system.datetime.parseexact?view=netcore-3.1 , http://net-informations.com/q/faq/stringdate.html , https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/standard/base-types/standard-date-and-time-format-strings?redirectedfrom=MSDN
Reflection: https://docs.microsoft.com/it-it/dotnet/visual-basic/programming-guide/concepts/reflection , https://docs.microsoft.com/it-it/dotnet/standard/attributes/retrieving-information-stored-in-attributes ,
http://net-informations.com/faq/net/reflection.htm , https://www.codemag.com/Article/0211161/Reflection-Part-1-Discovery-and-Execution , https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4Xt2o3oQMD0 , https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wfDFI9A56Gs
Asymptotic computational complexity: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Asymptotic_computational_complexity#:~:text=In%20computational%20complexity%20theory%2C%20asymptotic,of%20the%20big%20O%20notation. , https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Big_O_notation
Graphics object: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/desktop/winforms/advanced/getting-started-with-graphics-programming?view=netframeworkdesktop-4.8
Transforms: http://math.hws.edu/graphicsbook/c2/s1.html , http://math.hws.edu/graphicsbook/c2/s3.html ,
Charts: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chart , https://visme.co/blog/types-of-graphs/ , https://www.fusioncharts.com/charts/gauges
Statistical data presentation: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5453888/
_______________________________________________________________________________________
-
LESSON 04 - [14 Oct 2021]
VIDEO LESSONS:
Note: "OPT"
indicates optional video material for extra help: it can be skipped. Same for
homework, "OPT" denotes homework that can be skipped.
Theory
Lesson_04_Theory_01_MeasuresOfCentralTendency_Dispersion https://drive.google.com/file/d/1nbxS0IDwvedWQYv9JKxczwBYCHdAdglw/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_04_Theory_02_OnlineAlgoForVariance_Welford https://drive.google.com/file/d/1PN6TYEH4XO6NsYF2-9o6aZrRIYXYmkUC/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_04_Theory_03_Covariance_OnlineAlgo https://drive.google.com/file/d/1XcZXbrtPM-fmi3gJ0Zp72Qry7NO_sppx/view?usp=sharing
OPT
Lesson_04_Theory_04_GeneralizedMean https://drive.google.com/file/d/1nO_ama3jrWlLfQ6SgqGfoEpLBXBSZ16L/view?usp=sharing
OPT
Lesson_04_Theory_05_ArithmeticMean https://drive.google.com/file/d/1iCweHFvSi9yIt_JWxO_Fz1h5shvOrAxf/view?usp=sharing
OPT Lesson_04_Theory_06_Median https://drive.google.com/file/d/1aF13Houc7svk0bh9jnVqDXiRU0MoFM9n/view?usp=sharing
OPT Lesson_04_Theory_07_Mode https://drive.google.com/file/d/13dwz6P-HNTZxR_OsfMLk-AV1_bP6-Ijr/view?usp=sharing
OPT Lesson_04_Theory_08_NaiveCovariance_Variance https://drive.google.com/file/d/10_lDzwO5BjUlA--rVPvvc_Wo8k_DFAz5/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_04_Theory_09_QuickIntroLinearRegression https://drive.google.com/file/d/1qiJ8l7TgiSuyh3omiK031tH0QPasxv0u/view?usp=sharing
Computer applications, and language fundamentals for
statistical algos
Lesson_04_Apps_01_WorldWindowToDeviceVieportTransform https://drive.google.com/file/d/1jB602QC-CfCaZcMrNR793YWrZX2krYWR/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_04_Apps_02_Transform_ManualMethodExample https://drive.google.com/file/d/1U24jxMgfAhmDv8yoDIWMR0ErR4WX4Zf3/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_04_Apps_03_InteractiveDeviceViewport https://drive.google.com/file/d/1UiSnUoZzwftjxmxynBq8QkLlZZr8hX0B/view?usp=sharing
OPT Lesson_04_Apps_04_InteractiveWorldWindow https://drive.google.com/file/d/1cZe_SsBeEB5G9osrz9v3obzJjIc7p_tu/view?usp=sharing
OPT Lesson_04_Apps_05_TransformMatrix_GraphicsTransform https://drive.google.com/file/d/1MF1gZgR3WDWaC1FS3W7qMXWZP1fEexgR/view?usp=sharing
OPT Lesson_04_Apps_06_WordCloudExample https://drive.google.com/file/d/1aJjume4UrVqfbrmAuqEdapnYcmhLgM4I/view?usp=sharing
HOMEWORK / ASSIGNMENTS (to be published by the student on the personal blog) : [DATE DUE: post your link within 24 Oct 2021, or -1 penalty on final grade may apply ]
Researches about theory (R)
5_R. Explain a possibly unified conceptual framework to obtain all most common measures of central tendency and of dispersion using the concept of distance (or "premetric", or similarity in general). Discuss why it is useful to discuss these concepts introducing the notion of distance. Finally, point out the difference between the mathematical definition of "distance" and the properties of the "premetrics" useful in statistics, pointing out trhe most important distances, indexes and similarity measures used in statistics, data analysis and machine learning (such as for instance; Mahalanobis distance, Euclidean distance, Minkowski distance, Manhattan distance, Hamming distance, Cosine distance, Chebishev distance, Jaccard index, Haversine distance, Sørensen-Dice index, etc.).
Applications / Practice (A) [work
on this at least 30' a day, all days]
6_A. (For this exercises use only 1 language
chosen between C# or VB.NET, according to your preference)
Prepare separately the following charts: 1) Scatterplot, 2)
Histogram/Column chart [in the histogram, within each class interval, draw also
a vertical colored line where lies the true mean of the observations falling in
that class] and 3) Contingency table, using the graphics object and its methods
(Drawstring(), MeasureString(), DrawLine(), etc).
Use them to represent 2 numerical variables that you select from a CSV file. In particular,
in the same picture box, you will make at least 2 separate charts: 1 dynamic
rectangle will contain the contingency table, and 1 rectangle (chart) will
contain the scatterplot, with the histograms/column charts and rug plots drawn
respectively near the two axis (and oriented accordingly).
Researches about applications (RA)
4_RA. Do a personal research about the real world window to viewport transformation, and note separately the formulas and code which can be useful for your present and future applications.
OPTIONAL applications
Translate the last exercises 6_A to web browser
applications, in plain javascript (no "third party libraries", check also
https://www.datatime.eu/public/cybersecurity/JSTutorial/ for some
progressive examples) [+1 extra point for this optional part.].
REFERENCES / SOURCES / USEFUL LINKS:
Additional useful readings on statistical theory:
Summary stats https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Summary_statistics , https://statistics.laerd.com/statistical-guides/measures-central-tendency-mean-mode-median.php#:~:text=A%20measure%20of%20central%20tendency,also%20classed%20as%20summary%20statistics . , https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/2554243/understanding-the-mean-minimizes-the-mean-squared-error , https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/200282/explaining-mean-median-mode-in-laymans-terms , http://dida.fauser.edu/calcolo/calcol3/valmedi.htm#:~:text=Una%20propriet%C3%A0%20caratteristica%20della%20mediana,scarti%20da%20qualunque%20altro%20valore
Distances
https://people.revoledu.com/kardi/tutorial/Similarity/MahalanobisDistance.html
https://www.machinelearningplus.com/statistics/mahalanobis-distance/
https://medium.com/@kunal_gohrani/different-types-of-distance-metrics-used-in-machine-learning-e9928c5e26c7
https://towardsdatascience.com/9-distance-measures-in-data-science-918109d069fa
Dimensional analysis: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dimensional_analysis
Metrics: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metric_(mathematics) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metric_(mathematics)#Premetrics
Central tendency https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Central_tendency#Solutions_to_variational_problems
Discrete distance https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Discrete_space
Dispersion https://statistics.laerd.com/statistical-guides/measures-of-spread-range-quartiles.php
Variance https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Variance , https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/239379/what-is-the-difference-between-mean-squared-deviation-and-variance , https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Squared_deviations_from_the_mean , https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/711135/derivation-of-runningonline-variances-formula
Variance algos https://it.wikipedia.org/wiki/Algoritmi_per_il_calcolo_della_varianza
For applications
Running Mean and Variance https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/20593/calculate-variance-from-a-stream-of-sample-values , https://www.johndcook.com/blog/standard_deviation/
Transforms http://math.hws.edu/graphicsbook/c2/s3.html , https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transformation_matrix#/media/File:2D_affine_transformation_matrix.svg
Matrices https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/desktop/winforms/advanced/why-transformation-order-is-significant?view=netframeworkdesktop-4.8
http://csharphelper.com/blog/2015/12/draw-round-circles-in-a-scaled-coordinate-system-in-c/
Web scraping https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Web_scraping
_______________________________________________________________________________________
-
LESSON 05 - [21 Oct 2021]
VIDEO LESSONS:
Note: "OPT"
indicates optional video material for extra help: it can be skipped. Same for
homework, " OPT" denotes homework that can be skipped.
Theory
OPT Lesson_05_Theory_01_VarianceDecomposition_CoefficientOfDetermination https://drive.google.com/file/d/1beOMXQbzW_f99vaEMQWU81qvN9XeWGwa/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_05_Theory_02_MeasureTheory_ProbabilityAxioms https://drive.google.com/file/d/1MmJoRZKqXibg7vA3z7QWkmAUbBB7HVv7/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_05_Theory_03_ParametricInference_InductiveReasoning https://drive.google.com/file/d/1yR3Rr4an2eQpCVFyxm91M_DYzgfSyAAu/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_05_Theory_04_RoleOfProbabilityInStatistics https://drive.google.com/file/d/1DOyD8x4O2llZc_NqhGtFFEKrCPKMRTGV/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_05_Theory_05_ProbabilitySpaceAndStatistics_RandomVariables https://drive.google.com/file/d/1eQLx-K8chF3Mdrwu0mSTkl7wrQ7cT94S/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_05_Theory_06_QuickIntroToLebesgueIntegralAndMeanVarianceOfRandomVariables https://drive.google.com/file/d/1AhsZ6prIqAHu06fx1l2Cxokq60EnQ7g_/view?usp=sharing
Computer applications, and language fundamentals for
statistical algos
(expand your library collection by refining and adding new
functionalities for charting, eg. try 3D objects and shading)
HOMEWORK / ASSIGNMENTS (to be published by the student on the personal blog) : [DATE DUE: send your link within 31 Oct 2021, or -1 on final grade penalty may apply]
Researches about theory (R)
6_R. Think and explain in your own words what is the role that probability plays in Statistics and the relation between the observed distribution and frequencies their "theoretical" counterparts. Do some practical examples where you explain how the concepts of an abstract probability space relate to more "concrete" and "real-world" objects when doing statistics.
7_R. Explain the Bayes Theorem and its key role in statistical induction. Describe the different paradigs that can be found within statistical inference (such as"bayesian", "frequentist" [Fisher, Neyman]).
Applications / Practice (A) [work
on this at least 30' a day, all days]
7_A. Given 2 variables
taken from a CSV file compute and represent the statistical
regression lines (X to Y and viceversa) and the scatterplot.
Optionally, represent also the histograms on the "sides" of the chart (one could
be draw vertically and the other one horizontally, in the position that you
prefer).
[Remember that all our charts must alway be done within "dynamic viewports"
(movable/resizable rectangles). No third party libraries, to ensure ownership of
creative process. May choose the language you prefer.].
Researches about applications (RA)
5_RA. Do a web research about the various methods to
generate, from a Uniform([0,1)), all the most important random variables
(discrete and continuous). Collect all source code you think might be useful
code of such algorithms (keep credits and attributions wherever applicable), as
they will be useful for our next simulations.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_probability_distributions
https://www.cs.wm.edu/~va/software/park/park.html
https://www.johndcook.com/blog/2010/05/03/c-random-number-generation-code/
https://homeweb.csulb.edu/~tebert/teaching/lectures/552/variate/variate.pdf
https://www.jstor.org/stable/1402590
https://www.icosaedro.it/phplint/generating-statistical-distributions/index.html
etc...
REFERENCES / SOURCES / USEFUL LINKS:
Additional useful readings on theory:
Paradigms:
https://degreesofbelief.roryquinn.com/statistics-bayesian-frequentist
https://www.nhh.no/globalassets/departments/business-and-management-science/research/lillestol/statistical_inference.pdf
https://faculty1.coloradocollege.edu/~sjanke/Slides/Bayes_SJ.pdf
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Frequentist_inference
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bayesian_inference#In_frequentist_statistics_and_decision_theory
Inductive reasoning ;https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inductive_reasoning
Statistical induction https://www.wikilectures.eu/w/Statistical_Induction_Principle#:~:text=Inductive%20statistics%20is%20way%20for,in%20a%20inductive%20way .
Frequentist and Bayesian https://www.probabilisticworld.com/frequentist-bayesian-approaches-inferential-statistics/ , https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/mathematics/18-05-introduction-to-probability-and-statistics-spring-2014/readings/MIT18_05S14_Reading20.pdf , https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Frequentist_inference , https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bayesian_inference ,
Variance Decomposition https://murraylax.org/rtutorials/regression_anovatable.pdf
Coefficient of Determination https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coefficient_of_determination
Correlation coefficient https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pearson_correlation_coefficient
Cauchy Schwarz https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cauchy%E2%80%93Schwarz_inequality
Mathematical stats https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mathematical_statisticss
Measure Theory https://terrytao.files.wordpress.com/2011/01/measure-book1.pdf , https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Measure_(mathematics )
Measurable function https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Measurable_function
Lebesgue measure https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lebesgue_measure
Borel Measure https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Borel_measure
Measure space https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Measure_space
Sigma algebra https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/%CE%A3-algebra
Probability space https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Probability_space , https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/3205017/what-is-the-space-of-random-variables , https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/18198/what-are-the-sample-spaces-when-talking-about-continuous-random-variables , https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/264260/what-is-the-difference-between-sample-space-and-random-variable , https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computer-science/6-042j-mathematics-for-computer-science-fall-2010/readings/MIT6_042JF10_chap17.pdf
Probability measure https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Probability_measure
Random Variable https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Random_variable
pdf https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Probability_density_function
cdf https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cumulative_distribution_function
videos:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZJsOOCghQJ0 "Cumulative Distribution Function (1 of 3: Definition)"
Lebesgue Stielties integral https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lebesgue_integration , https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lebesgue%E2%80%93Stieltjes_integration , https://matheducators.stackexchange.com/questions/5981/what-is-a-good-way-to-explain-the-lebesgue-integral-to-non-math-majors , https://www.whitman.edu/Documents/Academics/Mathematics/2017/Wang.pdf , http://www.math.nagoya-u.ac.jp/~richard/teaching/s2017/Nelson_2015.pdf , https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/1267330/on-the-horizontal-integration-of-the-lebesgue-integral
Fubini-Tonelli https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fubini%27s_theorem
Layer cake representation https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Layer_cake_representation , https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/998633/how-is-fubinis-theorem-used-in-the-following-proof , https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/338275/proof-of-int-0-inftyptp-1-mu-xfx-geq-t-d-mut-int-0-inft
Simple function https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/2481592/step-function-vs-simple-function
Dirichlet https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nowhere_continuous_function
Random Variables, generation https://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/books/ftp/ch5f_slides.pdf , https://encyclopediaofmath.org/wiki/Generating_random_variables , https://web.mit.edu/urban_or_book/www/book/chapter7/7.1.3.html , https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-generate-random-variables-from-scratch-no-library-used-4b71eb3c8dc7 , http://www.columbia.edu/~mh2078/MonteCarlo/MCS_Generate_RVars.pdf , http://www.stat.tamu.edu/~jnewton/604/chap3.pdf
Inverse transform sampling https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inverse_transform_sampling
Rejection sampling https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rejection_sampling
Ziggurat algo https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ziggurat_algorithm
http://www.jstatsoft.org/v05/i08/paper , https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/6287927.pdf
Box Muller transform https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Box%E2%80%93Muller_transform
Other normal http://home.iitk.ac.in/~kundu/paper104.pdf
Monte Carlo methods https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monte_Carlo_method
For applications
Definite integral video https://www.khanacademy.org/math/ap-calculus-ab/ab-integration-new/ab-6-3/v/riemann-sums-and-integrals , https://www.khanacademy.org/math/ap-calculus-ab/ab-integration-new/ab-6-3/a/definite-integral-as-the-limit-of-a-riemann-sum
https://mathinsight.org/calculating_area_under_curve_riemann_sums
https://www.emathhelp.net/calculators/calculus-2/riemann-sum-calculator/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Riemann_sum
https://www.desmos.com/calculator/tgyr42ezjq?lang=it
Running Regression https://www.johndcook.com/blog/running_regression/
One pass skeweness and kurtosis https://www.johndcook.com/blog/skewness_kurtosis/
_______________________________________________________________________________________
-
LESSON 06 - [12 Nov 2020]
VIDEO LESSONS:
Note: "OPT"
indicates optional video material for extra help: it can be skipped. Same for
homework, " OPT" denotes homework that can be
skipped.
Theory
Lesson_06_Theory_01_RecapAndProbabilityDistribution https://drive.google.com/file/d/1_mIeSn8vJBh3u82JyjZmzVAi34EATop9/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_06_Theory_02_SequencesOfRandomVariables_ConvergenceInDistribution https://drive.google.com/file/d/1SZZflBa6ek20bxZeFAqph1JYg3hKbtHX/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_06_Theory_03_ConvergenceInProbabilityAndQuickIntroToLLN https://drive.google.com/file/d/1tbRiLN6w2RGg172IbcEdUzDsHOqX2Bj4/view?usp=sharing
OPT (some
additional explanation for exercise 13_A) Lesson_06_Theory_04_ExerciseOnLLN https://drive.google.com/file/d/1etyfP_jm5N3p8aX1qmjbLmJUVs7b9STT/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_06_Theory_05_MeanVarianceOfSampleMean https://drive.google.com/file/d/1XBSvmDylVTNpo_RG8vwuE8ouizRM1gCs/view?usp=sharing
Computer applications, and language fundamentals for statistical algos
(revise and refine your previous programs and libraries)
HOMEWORK / ASSIGNMENTS (to be published by the student on the personal blog) : [DATE DUE: send your link within 7 Nov 2021, or -1 on final grade penalty may apply]
Researches about theory (R)
8_R.
Do a research about the following topics:
- The law of large numbers LLN, the various definitions of convergence
- The convergence of the Binomial to the normal and Poisson distributions
- The central limit theorem [in anticipation of a topic we will study later]
Applications / Practice (A) [work on this at least
30' a day, all days]
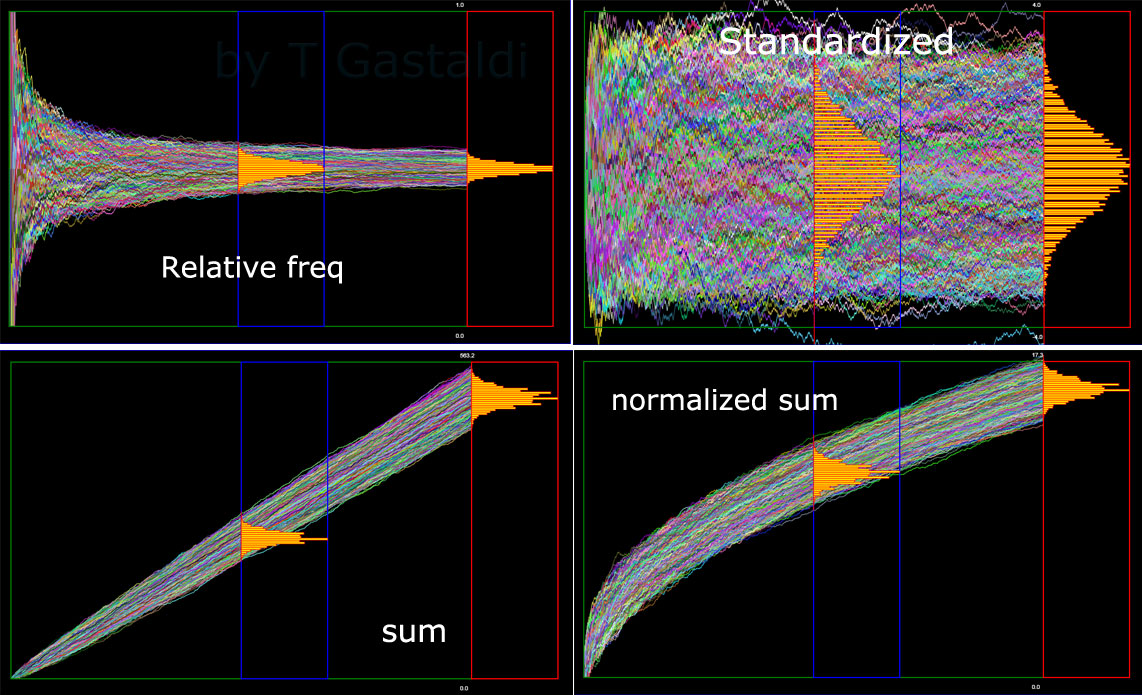
8_A. Exercise (also partially described in video 04)
Generate and represent m "sample paths" of n point each (m, n are program
parameters), where each point represents a pair of:
time index t, and relative frequency of success f(t),
where f(t) is the sum of
t Bernoulli random variables with distribution B(x, p) = p^x(1-p)^(1-x)
observed at the various times up to t: j=1, ..., t..
At time n (last time) and one other chosen inner time 1<j<n (where j is a
user parameter) represent with a histogram the distribution of f(t).
See
also what happens if you replace the relative frequency
f(t) with the absolute
frequency n(t) or by standard relative frequency: (f(t)-p) /
sqrt(p(1-p)/t) [ or some "normalized" sum of bernoulli r.v.'s, eg. n(t)
/ Math.sqrt(t) ].
Comment briefly
on the convergence results you see.

(The general scheme of this exercise, will also be "reused" in next homeworks
where we will consider other more interesting stochastic processes.)
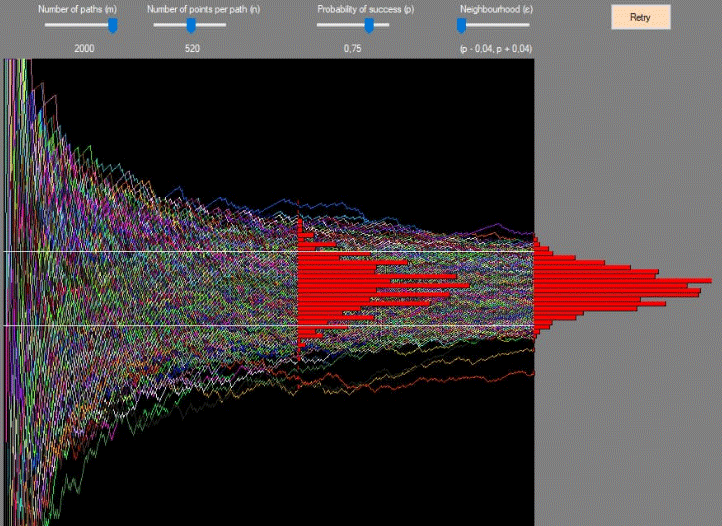 (source:
homework screenshot by student Lorenzo Zara, year 2020)
(source:
homework screenshot by student Lorenzo Zara, year 2020)
Researches about applications (RA)
6_RA. Do a
web research about the various methods proposed to compute the running
median (one pass, online algorithms).
Store (cite all sources and attributions) the algorithm(s) that
you think is(are) a good candidate, explaining briefly how it works and possibly
try
a quick demo.
REFERENCES / SOURCES / USEFUL LINKS:
Additional useful readings on theory:
Probability distribution https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Probability_distribution , https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/489948/difference-between-uniform-laws-of-large-numbers-and-law-of-large-numbers?rq=1 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Probability_mass_function , https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Probability_density_function , https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cumulative_distribution_function
Convergence https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l_YZ096WH74 , https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZKqzA81Nz2Y https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/2230/convergence-in-probability-vs-almost-sure-convergence , https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/3776889/interpreting-almost-sure-convergence , https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/141219/almost-sure-convergence-does-not-imply-complete-convergence, https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/2926296/weak-convergence-of-measures-implying-almost-sure-convergence-of-random-variable
Variance of relative frequency https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/1526230/variance-of-relative-frequency#:~:text=If%20we%20perform%2010%20trials,1%E2%88%92p)%2F10.
LLN https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Law_of_large_numbers , https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/47310/weak-law-of-large-numbers-redundant https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/22557/central-limit-theorem-versus-law-of-large-numbers , https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/45695/conditions-in-law-of-large-numbers?rq=1 , https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/29882/when-does-the-law-of-large-numbers-fail?rq=1 , https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/24562/why-law-of-large-numbers-does-not-apply-in-the-case-of-apple-share-price?rq=1
For applications
Median https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/134/algorithms-to-compute-the-running-median http://www.dsalgo.com/2013/02/RunningMedian.php.htmll https://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs2110/2009su/Lectures/examples/MedianFinding.pdf , https://github.com/GuyKomari/Median-Online-Algorithm
_______________________________________________________________________________________
-
LESSON 07 - [4 Nov 2020]
VIDEO LESSONS:
Note: "OPT"
indicates optional video material for extra help: it can be skipped. Same for
homework, "OPT"
denotes homework that can be skipped.
Theory
Lesson_07_Theory_01_ConcentrationInequalities_Markov https://drive.google.com/file/d/1gnXs8gwUEt5GgNoxmjpFENY7w8SQHcx1/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_07_Theory_02_ConcentrationInequalities_Chebyshev_LLNProof https://drive.google.com/file/d/1QtYA2hgZLaaA3hZg_VL8Pl-U84MqK-CX/view?usp=sharing
OPT Lesson_07_Theory_03_AlmostSureConvergence_BorelCantelli https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Db4wEwHhgMae2BPJ5f049xLFNh2YLHkk/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_07_Theory_04_GlivenkoCantelli_UniformConvergenceOfEmpiricalCDF https://drive.google.com/file/d/1yIEmHhqe0h1i-nBg_vCcJ0yzSAjfav6a/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_07_Theory_05_Standardization_QuickIntroToCLT https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Oosog1d1O461OlK4mOwTisrUmR_HqrEs/view?usp=sharing
Computer applications, and language fundamentals for statistical algos
reorgarnize and clean up your previous code and applications
HOMEWORK / ASSIGNMENTS (to be published by the student on the personal
blog) : [DATE DUE: send your link within 14 Nov 2021, or -1 on final grade
penalty may apply]
Researches about theory (R)
9_R. History and derivation of the normal distribution. Touch, at least,
the following three i mportant perspectives, putting them into an historical
context to understand how the idea developed:
1) as approximation of binomial (De Moivre)
2) as error curve (Gauss)
3) as limit of sum of independent r.v.'s (Laplace)
some video sources:
"The Evolution of the Normal Distribution" https://www.maa.org/sites/default/files/pdf/upload_library/22/Allendoerfer/stahl96.pdf
"The Normal Distribution: A derivation from basic principles" https://www.alternatievewiskunde.nl/QED/normal.pdf
"A Derivation of the Normal Distribution" https://web.sonoma.edu/users/w/wilsonst/papers/Normal/default.html
https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/384893/how-was-the-normal-distribution-derived
"Normal Distributions: The History of the Discovery of Normal Distributions" https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BXof869EC68
"Normal Distribution Example and History Part 1" https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XUT5Oadidbw
"History of the Normal Distribution" https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-ftS9UqdA-g
"Normal Distribution, Why is it "Normal"? " https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nyibbuGFsr8
"Normal distribution's probability density function derived in 5min" https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ebewBjZmZTw
"The Normal Distribution (1 of 3: Introductory definition)" https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mHTp7azBhGs
etc.
Applications / Practice (A) [work on this at least
30' a day, all days]
9_A_1. Create a simulation with graphics to convince yourself of the uniform convergence of the empirical CDF to the theoretical distribution (Glivenko-Cantelli theorem). You may use a simple random variable of your choice for such a demonstration.
https://www.datatime.eu/public/cybersecurity/jsTutorial/22_GlivenkoCantelli.html
9_A_2. Generate sample paths of jump processes which at each time
considered t = 1, ..., n perform jumps computed as:
- σ R(t)
(and/or divide by sqrt(1/t) in case you want to make constant the variance at
each time by
"normalizing" the sum, or divide by sqrt(1/n) in order to obtain
standard deviation = σ at last time [the so called "scaling limit"])
where R(t) is a [-1,1] Rademacher random
variable (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rademacher_distribution).
- σ Z(t), where Z(t) is a N(0,1) random
variable (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Normal_distribution)
(and/or divide by sqrt(1/t) in case you want to make constant the variance at each time by "normalizing" the sum, or divide by sqrt(1/n) in order to obtain standard deviation = σ at last time )
and see what happens as n (simulation parameter, denoting the number of jumps, or subdivision in the "scaling limit") becomes larger.
[As
before, at time n (last time) and one other chosen inner time 1<j<n (j is a
program parameter) create and represent with histogram the distribution of the
process ]

Researches about applications (RA)
7_RA Do a research about the random walk process and its properties. Compare
your finding with your applications drawing your personal conclusions. Explain
based on your exercise the beaviour of the distribution of the stochastic
process (check out "Donsker's invariance principle"). What are, in particular,
its mean and variance at time n ?
REFERENCES / SOURCES / USEFUL LINKS:
Additional useful readings on theory:
Probability: Theory and Examples, Rick Durrett https://services.math.duke.edu/~rtd/PTE/PTE5_011119.pdf
MIT Fundamentals of Probability https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computer-science/6-436j-fundamentals-of-probability-fall-2018/lecture-notes/MIT6_436JF18_lec04.pdf
Markov inequality https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Markov%27s_inequalityy
Chebyshev inequality https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chebyshev%27s_inequality
"Weak Law of Large Numbers" from MIT https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3eiio3Tw7UQ
Borel Cantelli https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Borel%E2%80%93Cantelli_lemma , https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/486885/converge-of-scaled-bernoulli-random-process
Simplest proof of strong LLN https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/3068125/proofing-the-strong-law-of-large-numbers
https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/406226/central-limit-theorem-implies-law-of-large-numbers?rq=1
Infinite Monkey https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Infinite_monkey_theorem
Law of the unconscious statistician
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Law_of_the_unconscious_statistician
Glivenko-Cantelli Theorem https://mathigon.org/course/intro-statistics/empirical-cdf-convergence , https://www.stat.berkeley.edu/~bartlett/courses/2013spring-stat210b/notes/8notes.pdf , http://users.stat.umn.edu/~helwig/notes/den-Notes.pdf
http://home.uchicago.edu/~amshaikh/webfiles/glivenko-cantelli_topics.pdf
For applications
Random Walk https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Random_walk , http://www.math.caltech.edu/~2016-17/2term/ma003/Notes/Lecture16.pdf
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rademacher_distribution
_______________________________________________________________________________________
LESSON 08 -
[11 Nov 2021]
STREAMING or VIDEOS LESSONS:
Note: "OPT"
indicates optional video material for extra help: it can be skipped. Same for
homework, "OPT "
denotes homework that can be skipped.
Theory
"OPT"
Lesson_08_Theory_01_AlmostSurely_ProbabilityZero https://drive.google.com/file/d/1WTh5uDhPCBHJOGiWrlCu-Zk1_F74W1r5/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_08_Theory_02_OrderStatistics https://drive.google.com/file/d/1M_llkCcuDl1sAx7EMgwVW7JkRO5HegIc/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_08_Theory_03_Quantiles https://drive.google.com/file/d/1ZvhQsMh7fRKUchi9-7aTAQuNxCnf9Fb9/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_08_Theory_04_QuantileFunction_GeneralizedInverse https://drive.google.com/file/d/1nzQjbU9l-parcpgGcP6yJ1mAIh_cDsiM/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_08_Theory_05_OrderStatistics_Density https://drive.google.com/file/d/1jaxaDQRvuxvAdHkF-18lxx0Zn8Xz8KX_/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_08_Theory_06_OrderStatistics_CDF https://drive.google.com/file/d/191v43xoMG5q05oAqamkwNXNEgVQm9fbH/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_08_Theory_07_Ranks https://drive.google.com/file/d/1U4v5nf1cGBFjjQhy8_5BcPj9CmL3J5a6/view?usp=sharing
Computer applications, and language fundamentals for statistical algos
[revise you stochastic process simulator and your CSV parser and statistics
application]
HOMEWORK / ASSIGNMENTS (to be published by the student on the personal
blog) : [DATE DUE: send your link within 21 Nov 2021, or -1 on final grade
penalty may apply]
Researches about theory (R)
10_R. Distributions of the order statistics: look on the web for the most simple (but still rigorous) and clear derivations of the distributions, explaining in your own words the methods used.
11_R. Do a research about the general correlation coefficient for ranks and the
most common indices that can be derived by it. Do one example of computation of
these correlation coefficients for ranks.
Applications / Practice (A) [work on this at least 30' a
day, all days]
Represent also the distributions of the following quantities (and any other
quantity that you think of interest):
- Distance (time elapsed) of individual jumps from the origin
- Distance (time elapsed) between consecutive jumps (the
so-called "holding times")
Researches about applications (RA)
8_RA. Find out on the web what you have just generated in the previous
application. Can you find out about all the well known distributions that
"naturally arise" in this process ?
Hints:
https://www.probabilitycourse.com/chapter11/11_1_2_basic_concepts_of_the_poisson_process.php
https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computer-science/6-262-discrete-stochastic-processes-spring-2011/course-notes/MIT6_262S11_chap02.pdf
https://towardsdatascience.com/the-poisson-distribution-and-poisson-process-explained-4e2cb17d459
Additional useful readings on theory:
Almost surely https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Almost_surely
General correlation coefficient https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rank_correlation
Ranking https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ranking#Ranking_in_statistics
https://us.humankinetics.com/blogs/excerpt/what-is-rank-order-correlation
videos:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DE58QuNKA-c ("How To...
Calculate Spearman's Rank Correlation Coefficient (By Hand)")
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gDNmhEBZAO8 ("Rank
Correlations: Spearman's and Kendall's Tau")
Quantile function
Quantile function https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quantile_function
Generalized Inverse https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/1801362/generalized-inverse-of-a-function
https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/210683/proof-that-quantile-function-characterizes-probability-distribution
https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/3378799/is-the-sample-quantile-unbiased-for-the-true-quantile
videos
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ASHPdWCPBXE ("Cumulative
Distribution Function (3 of 3: Locating quantiles)")
For applications
https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/325539/lambda-exponential-vs-poisson-interpretation/325662
http://www.it.uu.se/edu/course/homepage/fussmobb/ht06/computing/labb5.pdf
http://www.math.unl.edu/~sdunbar1/ProbabilityTheory/Lessons/Poisson/PoissonOld/poisson.shtml
Jump process https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jump_process
_______________________________________________________________________________________
- LESSON 09 - [18 Nov 2020]
STREAMING or VIDEOS LESSONS:
Note: "OPT"
indicates optional video material for extra help: it can be skipped. Same for
homework, "OPT "
denotes homework that can be skipped.
Theory
Lesson_09_Theory_01_StochasticProcessDefinition_DiscreteContinuousTimeState https://drive.google.com/file/d/1O9-TeP8fUQcH1w2EUECBrZ2WYpsb1WP1/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_09_Theory_02_StochasticProcess_SamplePaths https://drive.google.com/file/d/1jYeLdpVjdBOtja1-iD4WqoXsIfd0JApE/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_09_Theory_03_StationaryIncrements https://drive.google.com/file/d/1ovXcMp5bdhz42S4MihP24KxfjHAtKkIH/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_09_Theory_04_ContinuityInProbability https://drive.google.com/file/d/1P6uWx5RDhvOYyzBAygBvyekk3Ww4-1a6/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_09_Theory_05_ContinuityAlmostSure https://drive.google.com/file/d/1JociclFbsDPeHc3vzzEEKMIL0hm9cIk_/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_09_Theory_06_CADLAG_RightContinuousWithLeftLimit https://drive.google.com/file/d/1jhwEK0qhbw69a0yUv9h5nFZ1CGMyafpm/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_09_Theory_07_LevyProcess https://drive.google.com/file/d/1jHN4BwKpw6kKkvB88s-BzeFiNzoPc4jE/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_09_Theory_08_BrownianMotion https://drive.google.com/file/d/14aOEJUuFxMGWlbkZFt5DpO7fUaCF06m8/view?usp=sharing
Computer applications, and language fundamentals for statistical algos
[revise and refine your stat application and your stochastic process simulator]
HOMEWORK / ASSIGNMENTS (to be published by the student on the personal
blog) : [DATE DUE: send your link within 28 Nov 2021, or -1 on final grade
penalty may apply]
Researches about theory (R)
12_R.What is the "Brownian motion" and what is a Wiener process. History, importance, definition and applications (Bachelier, Wiener, Einstein, ...):
13_R. An "analog" of the CLT for stochastic process: the standard Wiener process as "scaling limit" of a random walk and the functional CLT (Donsker theorem) or invariance principle. Explain the intuitive meaning of this result and how you have already illustrated the result in your homework.
Set, collection, class, family, sequence difference https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/223405/can-elements-in-a-set-be-duplicated , https://stackoverflow.com/questions/821079/when-to-use-set-vs-collection#:~:text=The%20practical%20difference%20is%20that,unordered%2C%20while%20Collection%20does%20not .
, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Partially_ordered_set , https://www.samuel-drapeau.info/math/2015/10/04/family-vs-collection/#:~:text=Given%20a%20set%20X%2C%20a,of%20elements%20is%20not%20possible .
, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Subset , https://www.stat.auckland.ac.nz/~fewster/325/notes/ch1annotated.pdf , https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/604305/what-is-difference-between-stochastic-process-and-a-sequence-of-random-variables , https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/1593384/what-is-the-difference-between-an-indexed-family-and-a-sequence/1593393#:~:text=Formally%2C%20this%20sequence%20is%20a,I%20can%20be%20any%20set.&text=Here%20you%20can%20see%20that,the%20set%20of%20positive%20integers .
, https://mathworld.wolfram.com/Collection.html , https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/1601545/whats-the-definition-of-a-collection , https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/172966/what-are-the-differences-between-class-set-family-and-collection . https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Function_(mathematics )
, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary_relation , https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cartesian_product
Discrete and continuous time https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Discrete_time_and_continuous_time
Discrete and continuous state space https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Discrete-vs-continuous-time-and-discrete-vs-continuous-state-space-models_fig1_220053939 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stochastic_process
Stationary Independent Increments https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/476740/what-is-a-random-process-with-stationary-independent-increments
Independent increments of Poisson process https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/69498/how-to-prove-the-independent-and-stationary-increment-of-a-poisson-process
Continuity https://www.stat.cmu.edu/~cshalizi/754/notes/lecture-07.pdf , https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Continuous_stochastic_process, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sample-continuous_process#:~:text=In%20mathematics%2C%20a%20sample%2Dcontinuous,are%20almost%20surely%20continuous%20functions.
Levy Process https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/L%C3%A9vy_process
Wiener Process, Brownian Motion http://galton.uchicago.edu/~lalley/Courses/313/WienerProcess.pdf ,
https://galton.uchicago.edu/~lalley/Courses/313/BrownianMotionCurrent.pdf
http://www.math.uchicago.edu/~may/VIGRE/VIGRE2010/REUPapers/Dahl.pdf , https://www.ge.infn.it/~zanghi/FS/BrownTEXT.pdf
Ito integral
https://www.ie.bilkent.edu.tr/~mustafap/courses/TBII.pdf
Properties: https://www.math-berlin.de/images/stories/lecnotes_moerters.pdf
Non differentiability of BM https://quant.stackexchange.com/questions/10861/how-can-the-wiener-process-be-nowhere-differentiable-but-still-continuous
Diffusion process s https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diffusion_
Kolmogorov equations https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kolmogorov_equations , https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kolmogorov_equations_(Markov_jump_process , https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fokker%E2%80%93Planck_equation
Donsker theorem (functional central limit theorem) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Donsker%27s_theorem , https://encyclopediaofmath.org/wiki/Donsker_invariance_principle
______________________________________________________________________________________
-
LESSON 10 - [2 Dic 2020]
STREAMING or VIDEOS LESSONS:
Theory
Lesson_10_Theory_01_QuickIntroToSDE https://drive.google.com/file/d/1maWgfMHjUMtoK2aAORZHsoHE5ix4SKWy/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_10_Theory_02_GeometricBrownianMotionSDE https://drive.google.com/file/d/1dNFgsipYz9KVhHs7h7zUk_WDwIPWSoWC/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_10_Theory_03_QuickIntroToSolutionOfSDE_1 https://drive.google.com/file/d/1cY6VCO-7-s8xieKRh_OA0-Ven_fOclG9/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_10_Theory_04_QuickIntroToSolutionOfSDE_2 https://drive.google.com/file/d/1whpVDpOYSYypoGGki_3BxHbN-bF3TQ1s/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_10_Theory_05_SolutionForStandardBrownianMotion https://drive.google.com/file/d/1nlMSkhVJmvW41W4RshQi8sXHs696Cu5c/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_10_Theory_06_SolutionForGeneralBrownianMotion https://drive.google.com/file/d/1WjZ_64zT2EyScoQkWZIsQfufSyjEtful/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_10_Theory_07_Ornstein_Uhlenbeck_VasicekSDE https://drive.google.com/file/d/1bLByibiq20gza6WFNqygSHo0QiB3g4nh/view?usp=sharing
Lesson_10_Theory_08_Euler_Maruyama_Method https://drive.google.com/file/d/1XJkfymX26o_yK7AdVaGnS15q5RSdFSY0/view?usp=sharing
Computer applications, and language fundamentals for statistical algos
[revise and refine your applications and libraries, complete the mini thesis]
HOMEWORK / ASSIGNMENTS (to be published by the student on the personal
blog) : [DATE DUE: send your link within 16 Dec 2020, or -1 on final grade
penalty may apply]
Researches about theory (R)
- LESSON 11 - [9 Dic 2020]
[Skipped on students' request, to allow preparation for exam and completion of projects]
FINAL EXAM
Oral part: your blog contents
Written part: this year, instead of 2 midterms, we will simplify the procedure.
Each student
will instead produce a detailed "mini thesis" on 1 topic chosen from the following
list:
Collect all possible material from web sources about one single specific topic,
carefully indicating all sources and attributions.
Your “creativity” must be
directed not in “ creating” anything “new”, but in understanding, organizing the material in
the most logic and understandable way, paying attention on the math proofs and
details. Maximize simplicity and rigour at the same time, whenever possible.
Make sure to include:
1. Historical fact and motivation
2. Intuition
3. Full math details
4. Whatever additional material: demo, video, source code
(Make sure you check all main web sources and Q&A sites (YouTube, Khan academy,
wikipedia, wikidata, wikimedia commons, wikisource, stackexchange, quora,
reddit, ... specialized articles and sites, and quote all sources with the
respective links ...)
Topics:
1. Normal: history, motivation, all proofs, all most important “derived” distributions (chi
square, F Fisher, T Student)
2. Online algorithms (mean, variance, median, …): all details about numerical
stability, floating point issues, etc.
3. Lebesgue-Stieltjes integral: history, motivation, intuition, usage in probability theory,
all the math details
4. Central limit theorem: history, motivation, intuition, all the math details
5. Arithmetic Brownian Motion: history, motivation, intuition, usage, full math details
about all most important results
6. Geometric Brownian Motion: history, motivation, intuition, usage, full math details about
all most important results
7. Functional central limit theorem (invariance principle or Donsker’s theorem):
history, motivation, intuition, full math details
8. Itô integral (Itô calculus):
history, motivation, intuition, full math details about
all most important results
Final exam submission instructions:
1) Make sure you book the exam on Infostud
2) Send the following material at
statisticssapienza@gmail.com in 1 unique email, before the official exam
date (at least 3-7 days before)
-1 name, ID
-2 your "mini thesis" (a compressed file with a word doc): if you cannot send
it, just include a link for download
-3 Your blog link
-4 number of "discontinuity penalties" (homeworks not handed on time)
accumulated, if any
-5 brief "defense" of your work and study during the course
-6 your final proposed grade (possibly subtract "penalties", if any), based on
your perception of your performance with possible motivation
-7 optional. Two words on: How did you find this course ? What did you like and
how would you improve it ??
To speed things up, given the large number of students, if your grade proposal
will appear comparatively fair - given your researches online and your final
mini thesis - I will accept direcly that on the oral exam, otherwise we will go
through a more detailed examination for accurate assessment. (The oral exam will
be carried out in any case.)
When ready, send the email with the listed material and we will make an
appointment to do thehe oral
exam
[A word of caution (just in case):):
1) If material are essentially identical, in the sense that apart superficial
camuflages, they are obviously from the "same hand", they will all be nullified.
2) Please, do not book for the exam if you are not adequately prepared. For an
instructor, there are few things less more irritating than students "trying" to
pass exams without sufficient preparation or, even worse, trying to cheat using
work done by others.]
________________________________________
Useful general purpose free tools
Visual Studio (IDE)
https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/it/downloads/
https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/it/vs/older-downloads/ (include C# and VB.NET)
Video Player VLC (video player)
https://www.videolan.org/vlc/download-windows.it.html
Notepad++ (edit CSV data files)
https://notepad-plus-plus.org/downloads/
OBS Studio, open broadcaster software (to record video with screen and audio/cam)
https://obsproject.com/
Autodesk SketchBook (to make drawings)
https://sketchbook.com/
MP4Tools (simple mp4 cut/join)
https://www.mp4joiner.org/en/
JavaScript Tutorial for students https://www.datatime.eu/public/cybersecurity/jsTutorial/
Visual studio code
https://code.visualstudio.com/
[free]
WebStorm (Web dev)
[not free]
https://www.jetbrains.com/webstorm/promo/?source=google&medium=cpc&campaign=9641686227&gclid=CjwKCAjwtfqKBhBoEiwAZuesiB05XZrJPP0mypXfXzxuRqaqbANGtnp9o_BSQ_t3bnl14aBGbRbDMBoCfmsQAvD_BwE
HTML Corrector:
https://www.htmlcorrector.com/
HTML Validator:
https://www.freeformatter.com/html-validator.html
Spell check:
https://spellcheckplus.com/